|
Keywords:
|
Arrhythmias,
Ventricular fibrillation, Electrocardiography, Antiarrhythmic agents, Sudden
death
|
|
Disclosure Block:
|
T. Tada, None; K.F. Kusano,
None; S. Nagase, None; K. Banba, None; N.
Nishii, None; A. Watanabe, None; Y. Sakai,
None; M. Murakami, None; K. Miyaji, None; K.
Nakamura, None; S. Sakuragi, None; T. Ohe, None.
|
|
Abstract:
|
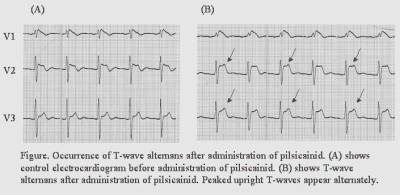
(Background)
T-wave alternans is a major predictor for cardiac sudden death in several
heart diseases. Manifest T-wave alternans (MTWA) is sometimes observed after
a sodium channel blocker administration in Brugada syndrome (BS), but little
is known about the occurrence of MTWA and clinical characteristics in
patients with Brugada syndrome. (Methods and Results) We administered
pilsicainide chloride, a class Ic sodium channel blocker, to total 84 BS
patients (age 48.0 years, 1 female). Clinical ventricular fibrillation (VF)
was documented in 12 patients. Predictive indices for VF occurrence,
including family history of sudden death, late potentials (LP), SCN5A
mutation, induction of VF during EP study, and MTWA were examined. MTWA was
not observed before pilsicainide administration, but became apparent in 14
patients 5 minutes after administration (Fig.). MTWA positive patients had
significantly a higher prevalence of VF (50% vs. 7.1%, P<0.001). In
univariate analysis, LP also had significant predictive value (P=0.003),
however in multivariate analysis, MTWA appeared the only independent
predictor for VF occurrence (P=0.009). (Conclusion) MTWA after pilsicainide
administration is associated with the high risk for the VF occurrence.
|