|
Presentation Time:
|
11/15/2005 9:00:00 AM
|
|
Title:
|
Electrocardiographic Characteristics of T-Wave Alternans are
Surprsingly Similar in Ischemic and Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
|
|
Keywords:
|
Sudden death,Cardiomyopathies,Ventricular arrhythmia
|
|
Author Block:
|
Quan V Pham, Ottorino Costantini, David S Rosenbaum, Metrohealth
Campus, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH
|
|
Disclosure Block:
|
Q.V. Pham, None; O.
Costantini, None; D.S. Rosenbaum, None.
|
|
Unlabeled/unapproved:
|
There are no unlabeled/unapproved uses of drugs or products.
|
|
Microvolt T-wave alternans (TWA) is associated with increased risk
of sudden cardiac death (SCD). Since ventricular arrhythmias commonly arise
from the border zone of myocardial infarction, we hypothesized that TWA in
ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) is dependent on the location of myocardial
infarction (MI) and therefore would differ from non-ischemic cardiomyopathy
(N-ICM). Of 290 consecutive patients with cardiomyopathy and no previous
arrhythmias who underwent TWA tests for SCD risk stratification, 84 patients
had positive TWA tests, and 69 of these with LVEF ≤ 0.40 were
included in this study. TWA magnitude for each lead was defined as the
maximum amplitude of statistically significant TWA in that lead which was
more than 1 minute in duration and occurred at a heart rate ≤ 110
bpm. Patients with ICM (54%) and N-ICM (46%) were equally represented. In
patient with ICM, TWA magnitude was highest in the anterior precordial
leads (V2, V3, V4), irrespective of MI location as determined by
echocardiography or radionuclide imaging. Surprisingly, the ECG lead
distribution of TWA magnitude in the N-ICM patients was similar to the ICM
patients (figure). CONCLUSIONS: This is the first systematic
analysis of ECG distribution of TWA. In the ICM, TWA is not randomly
distributed, but rather is highest in the anterior precordial leads,
irrespective of MI location. Surprisingly, TWA is distributed similarly in
the N-ICM. These data suggests that TWA may not originate from a fixed
anatomical border zone. 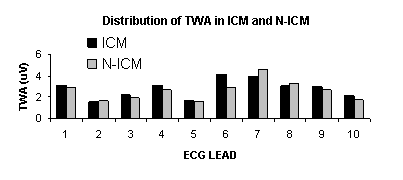
|
|
|
|