|
Title:
|
Combined Assessment of T-Wave Alternans and Plasma B-type
Natriuretic Peptide Can Predict Sudden Death in patients with Hypertrophic
Cardiomyopathy
|
|
Keywords:
|
Cardiomyopathies,Sudden death,Natriuretic peptides,
atrial,Electrocardiography
|
|
Author Block:
|
Masayuki Mizuno, Hirotaka Kawarai, Dai Yumino, Katsuya Kajimoto,
Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan
|
|
Disclosure Block:
|
M. Mizuno, None; H.
Kawarai, None; D. Yumino, None; K. Kajimoto,
None.
|
|
Unlabeled/unapproved:
|
There are no unlabeled/unapproved uses of drugs or products.
|
|
Sudden death (SD) in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) has remained
the most visible and devastating feature in the natural history of this
disease. Although any clinical markers of SD risk in HCM have been
proposed, available data at present suggest that there is no role for
non-invasive electrophysiological and neurohormonal markers to detect
patients (pts) at risk of SD in HCM. Therefore, we evaluate efficacy of
Microvolt-level T-Wave Alternans (TWA) and plasma B-type natriuretic
peptide (BNP) to identify high-risk pts of SD in HCM. Methods; In
consecutive 30 pts with HCM who were diagnosed and followed-up in our
hospital, we analyzed for TWA using the CH2000 system and plasma BNP at
baseline. Moreover, we evaluated a probability of SD (sudden cardiac death,
non-fatal cardiac arrest, or appropriate ICD interventions) in pts with HCM
during a mean follow-up of 20±6 months. Results; Among 30 HCM pts,
TWA showed positive in 15 pts and non-positive in 15 pts. In 15 pts with positive
TWA, 6 pts had sudden cardiac death (n=1), non-fatal cardiac arrest (n=2),
and ICD interventions (n=3). The probability of SD showed a significant
difference between pts with positive and non-positive TWA (P=0.04; figure).
Plasma BNP in pts (n=7) with SD was significantly higher than those (n=23)
without sudden death (664±380 vs. 188±120 pg/dl, p<0.001). A
combined assessment of positive TWA result and plasma BNP>300pg/dl
distinguished the high-risk pts of SD with a sensitivity of 72%, a
specificity of 100%, a positive predictive value (PV) of 100%, and a
negative PV of 92%. Conclusions; These results suggest that the
combined assessment of TWA and plasma BNP is useful for identifying
high-risk patients of SD in HCM. 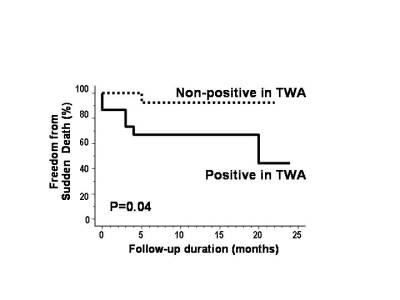
|
|
|
|